Project Description
Groundwater Flow Model and Flow Model Expansion for Hydrogeological Impact Evaluation Related to Operation of the Kern Water Bank and Pioneer Projects
Rosedale-Rio Bravo Water Storage District (On-Going)
 Project Objective
Project Objective
Evaluate the impacts of Kern Water Bank and Pioneer Project operations on the water budget and groundwater levels in the Kern Fan Area west of Bakersfield, California.
Project Approach
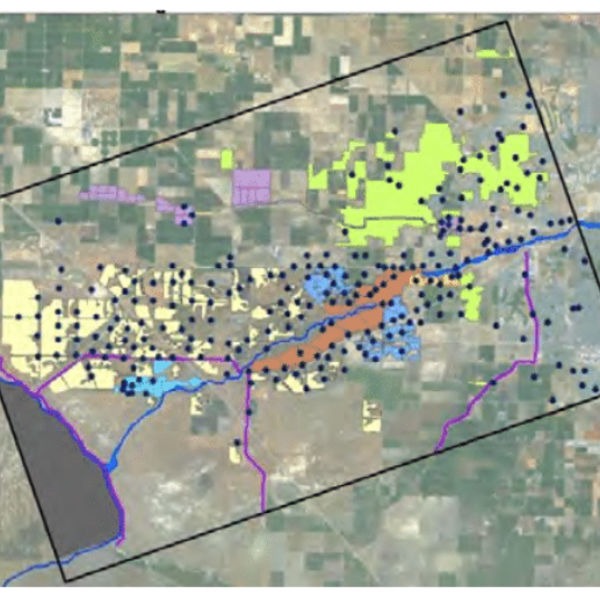
TH&Co developed a calibrated groundwater flow model of the Kern Fan Area using the USGS code MODFLOW. The original model area encompassed 160 square miles and included all
major groundwater production and recharge facilities in the area. The methodology to develop the model included hydrogeological basin characterization, numerical model development, formatting and input of groundwater production and recharge data, model calibration, and sensitivity analysis.
Other aspects of the model included:
- Model constructed with three layers and discretized with 200-ft grid cells.
- Includes more than 500 pumping wells and 266 recharge zones.
- Incorporates monthly stress periods.
- Incorporates a detailed analysis of pumping for agricultural operations.
- Successfully calibrated for the period from 1988 through 2015.
Project Results
The Kern Fan Area Model, which was determined to be successfully calibrated to industry standards by an outside peer reviewer, was used to analyze a “No-Project” operational scenario that quantified the impact of Kern Water Bank and Pioneer Project operations on groundwater levels in the area. This model continues to be used to guide decisions by a Joint Operating Committee for management of banking activities and determination of mitigation for private well pumpers.
Model Expansion
In 2017, the original model was expanded to address wells near the northern model boundary. The expanded model now encompasses 295 square miles and was successfully calibrated through 2016. Tasks for model expansion included extending existing cross sections, extending groundwater and structural contour maps, extending parameter maps, assigning new boundary conditions along the expanded boundary, updating existing input files, and recalibration of the model. The model is currently being updated on an annual basis to assess project groundwater production and recharge impacts.

